Timber - PVC - Aluminium - Windows, Doors & Conservatories in Hampshire
Window Energy Ratings (WERs) Explained: A Jargon-Free Guide
Window Energy Ratings (WERs) Explained: A Jargon-Free Guide
📌 The Jargon Buster: Key Takeaways
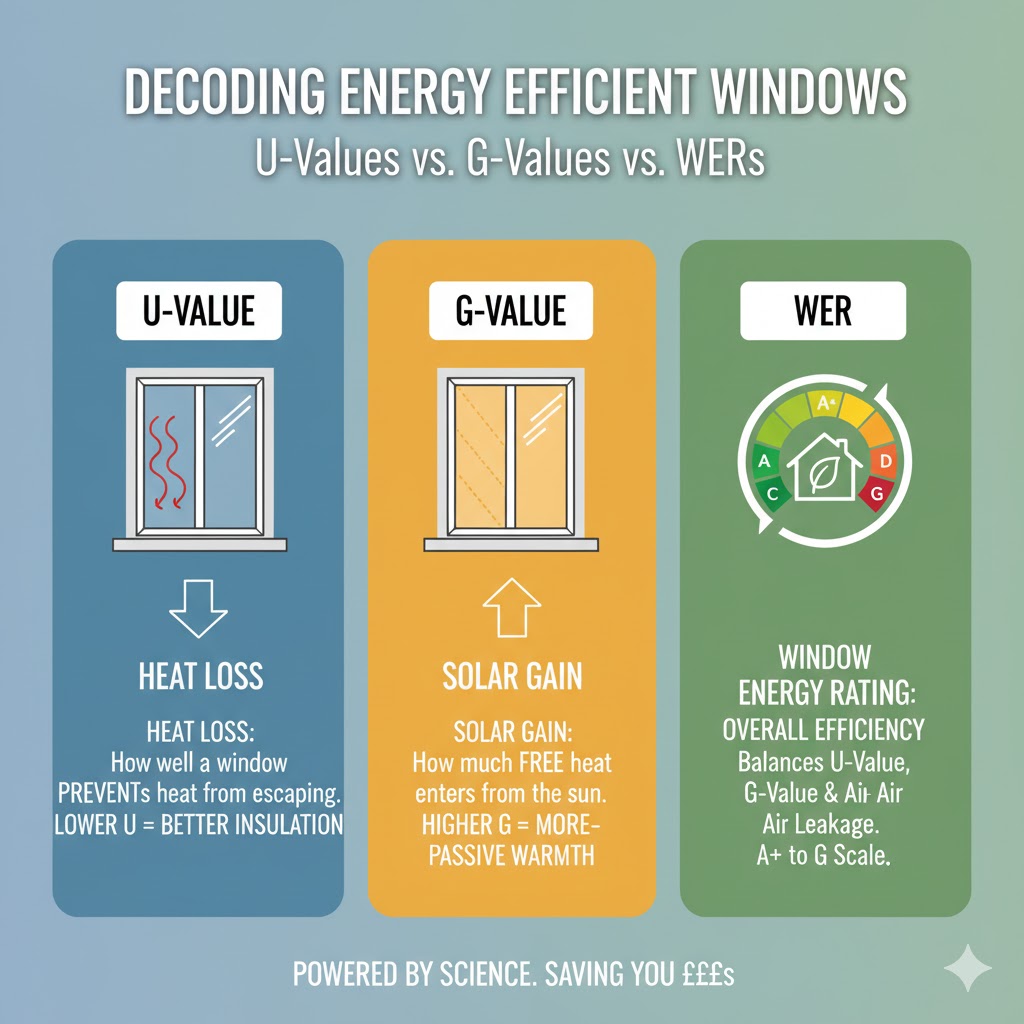
- U-Value (Insulation): Measures heat loss. Lower is better (0.8 is superb, 1.4 is standard). See the Part L Regulations Gov.uk.
- G-Value (Solar Gain): Measures free heat from the sun. High is good for winter heating; Low is good for preventing overheating.
- WER (Energy Rating): The consumer “Rainbow” label (A-G) managed by the BFRC External.
If you have ever tried to compare high-performance windows, you have likely encountered a wall of acronyms. Installers talk about WERs, architects specify U-values, and glass manufacturers mention G-values. It can be incredibly confusing.
Are they measuring the same thing? Is a higher number better, or a lower one? The truth is, these metrics often pull in opposite directions. A window that is excellent at keeping heat in might be terrible at letting heat out in summer.
Table of Contents
1. The Big 3 Metrics Compared
Use this quick reference table to understand which number you should be looking for.
Window Performance Matrix
What it Measures
Heat Loss. How fast heat escapes through the material.
The Goal
LOWER is Better. Aim for 1.2 W/m²K or lower.
Best For
Extensions, North-facing rooms, and keeping bills low.
What it Measures
Solar Gain. How much sun heat enters the room.
The Goal
Balance is Key. High for winter warmth, Low for summer cooling.
Best For
South-facing glass (Low G) or cold rooms (High G).
What it Measures
Overall efficiency balance (A++ to G scale).
The Goal
HIGHER is Better. Aim for ‘A’ or ‘A+’.
Best For
Standard replacement windows where simplicity is key.
2. U-Values Explained (The Critical Detail)
The U-value is the most scientific measure of insulation. It tells you: “If it is 1 degree colder outside than inside, how much heat will escape through one square metre of this window?”
However, you need to be careful. There are two types of U-value often quoted, and they are not the same.
- Ug (Centre Pane): Measures the glass only. Usually a very low, impressive number (e.g., 1.0).
- Uw (Whole Window): Measures the entire unit including the frame. This is usually higher (worse) because frames lose more heat than glass.
3. G-Values: Free Heat vs. Overheating
The G-value is expressed as a number between 0 and 1. A G-value of 0.75 means 75% of the sun’s heat enters the room.
The Conflict: In the UK winter, a high G-value is fantastic. It acts as free heating (Passive Solar Gain). However, in a highly insulated modern home with large south-facing glass (like bi-folds), a high G-value can be disastrous in summer, turning your room into a greenhouse.
If you are building a south-facing extension, you should ask for Solar Control Glass (low G-value) to prevent overheating.
4. Window Energy Ratings (WER)
The WER is the colourful “rainbow” sticker managed by the BFRC (British Fenestration Rating Council) Authority. It puts the U-value, G-value, and air leakage (L-value) into a formula: (Solar Gain) minus (Thermal Heat Loss) minus (Air Leakage).
Because it credits you for Solar Gain, it is possible for a window with slightly worse insulation (U-value) to get an ‘A’ rating simply because it lets in a huge amount of solar heat. This makes the WER perfect for comparing standard windows, but less useful for specialized architectural projects.
5. The Science: How Low-E Glass Works
How can a piece of glass stop heat? The secret is Low Emissivity (Low-E) Coating.
This is a microscopically thin layer of metal oxide applied to the inner surface of the glass. It acts as a selective mirror:
- Short-Wave Radiation (Sunlight): Passes straight through, lighting and warming your room.
- Long-Wave Radiation (Body Heat/Radiators): Bounces off the coating and reflects back into the room.
At KJM, we use “Soft Coat” Low-E glass, which offers better clarity and performance than older “Hard Coat” versions which often looked hazy.
6. The Future Homes Standard 2025
Building Regulations are tightening. The upcoming Future Homes Standard Gov.uk aims to ensure new homes produce 75-80% less carbon emissions. To achieve this, U-value targets are expected to drop drastically, likely towards 0.80 W/m²K for new builds.
This standard is difficult for double glazing to meet, paving the way for Triple Glazing to become the new norm. Installing high-spec triple glazing now ensures your home remains compliant and efficient for decades to come.
7. Frequently Asked Questions
No, the physical sticker is voluntary for the manufacturer. However, the window must still meet the minimum energy efficiency standards (B-rating/1.4 U-value) required by Building Regulations, regardless of whether it has a sticker on it.
No. The U-value only measures insulation. The ‘A’ rating (WER) is a better overall score because it accounts for insulation plus the free heat gained from the sun (G-value).
Yes. Timber and uPVC are naturally good insulators. Aluminium is conductive (cold), so modern aluminium windows use a “thermal break” (a plastic barrier inside the frame) to stop heat transfer and achieve high ratings.
Explore Our Triple Glazing Knowledge Hub
This article is part of our comprehensive series on high-performance windows. To understand the science, costs, and comparisons in more detail, start here:
- Certified Fire Doors: The Fire Stop Collection - 15 January 2026
- Premium Hardware for Profile 22 Doors: Ultion Sweet & Fab&Fix - 15 January 2026
- 2026 Design Trends: The 4 Window & Door Styles Defining the Year - 19 December 2025














